«A
Guide to Minimal Use of Neuroleptics: Why and How by Volkmar
Aderhold, MD and Peter Stastny, MD, June 2015
Rethinking
Antipsychotics(pdf) video Robert
Whitaker, February 2017
Open
Letter to
Norwegian
Psychiatric Society (Npf), TIPS,
UiO: NORMENT:
Norwegian Centre for Mental Disorders Research, OUS
Section for Treatment Research, Norwegian
Institute of Public Health, TIPS
early detection in psychosis
Copy:
Ingrid
Melle, Jan Olav Johannessen, Health
directorate [update]
Neuroleptics are used to ease symptoms and to prevent relapse with evidence at the beginning of the psychosis for a minority of patients. There is no evidence that antipsychotics promote "psychosocial functioning, professional functioning, and quality of life" (Buchanan et al 2009 PORT Treatment Recommendations). Recovery treatment still wins terrain and will be put into a historical context. Mike Slade et al. 2014 describes the implementation of recovery with both usage and abuse of the term. Too high doses of neuroleptics to too many patients over too long cause catastrophic poor treatment outcomes regarding recovery, disability / illness and chronic illness. A paradigm shift to lower doses for fewer patients over a shorter period of time with, for example, Open dialogue quadrupled recovery, reduces schizophrenia per year to one tenth and disability benefit / illness decreases to one third (5). Why is there still resistance despite very good treatment outcomes of recovery orientation such as Open dialogue (2)? How can a paradigm shift be made in the interest of patients' health and health professionals who want their efforts to benefit many more patients?
“In the 1950s, when the drugs we now call ‘antipsychotics’ first came along, psychiatrists recognised that they were toxic substances that happened to have the ability to suppress thoughts and emotions without simply putting people to sleep in the way the old sedatives did” (Joanna Moncrieff, MD 13. August 2013; Deniker P. Compr Psychiatry 1960 Apr;1:92-102.). Mainstream psychiatry was uncomfortable with the notion that its principle treatment worked by being a neurological toxin and transformed it into a sophisticated, treatment. At last the misleading expression “antipsychotics” was chosen.
The United Nations Special Rapporteur on the right to health Mr. Dainius Pūras has called for «World needs “revolution” in mental health care» to «enable a long overdue shift to a rights-based approach».“There is now unequivocal evidence of the failures of a system that relies too heavily on the biomedical model of mental health services, including the front-line and excessive use of psychotropic medicines, and yet these models persist” Mr. Dainius Pūras said.
Recovery is used in several meanings and has gained attention and has now become mainstream. WHO's Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2020 is with emphasis on recovery. The Norwegian Government's Strategy for Good Mental Health (2017-2022) "Mastering Life" is based on WHO's plan and The European Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2020 and. EU JOINT ACTION 2016. WHO project QualityRights initiative is improving quality, and promoting human rights. Both the United States, Canada, New Zealand, Australia, the UK and Ireland are building their national strategies on recovery. The Norwegian Mental Health Expansion Plan mentions the needs of the user/patient as a starting point, "mastering one's own life", "successful return to working life" and "entering into a social relationship with family and friends" (Ottar Ness 2015). The Norwegian Health Directorate has signalled to be positive. There is a long way to go to achieve a paradigm shift away from diagnosis and symptom treatment to the goal of recovery / recovery.
In Norway, e. g. Bjornestad, Jone et al. 2017 and 9 other researchers addressed the recovery perspective with the paper "Antipsychotic Treatment: Experiences of Fully Recovered Service Users". In collaboration with the NAPHA, 2013, "Recovery-oriented practices - a systematic knowledge-sharing" was launched. Illness Management and Recovery (IMR) is evidence-based treatment with good effect for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and severe depression. Open Dialogue was developed in Finland and is being used in several Scandinavian countries (2). In Valdres (Norway), the Odin Handbook (Open Dialogues in Network meetings) was developed. Drug-free treatment offerings at Åsgard Hospital in Tromsø (UNN) seem to have come a long way (1).
The discussion on drug-free offers in mental health care has exposed internal conflicts of psychiatry (Journal of Norwegian Medical Association No. 6, 21 March 2017). Do old truths stand for fall? Could it indicate changes? Are we heading for a paradigm shift?
Open dialogue reports more than 80% recovery (Seikkula et al. 2006) and the incidence of psychoses was reduced from 33 to 2 per 100,000 inhabitants per year (2, 5). Erika Jääskeläinen et al 2005 rapports that in 2001 recovery rate was 3,4 % and 56% of patients on disability allowances in Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966 , that is the same area before Open dialogue started up.
Svedberg et al. 2001 report 93% of patients on neuroleptics at any time and 75% ongoing. Open dialogue uses approx. 60% less neuroleptics (antipsychotics) for maintenance treatment and achieves more than 60% increase in recovery (2, 5). Open dialogue reduces disability allowance/sickness to one third.
[Tomi Bergström, Jaakko Seikkula et al. 2018 compare FEP Open dialogue patients with all FEP patients in Finland over a period of 19 years. Open dialogue (OD) uses neuroleptics for 20% of patients in the beginning, standard treatment (CG control group) 70%. 97,3 % of the CG get neuroleptics at some point. At the end 36% of OD patients use neuroleptics, for CG it is 81%. Disability allowance, readmission and patients under treatment halves with OD (20).]
The incidence of recovery in schizophrenia ranges between 4% and 20% (Warner 2004, Lieberman et al. 2008, Bertelsen et al. 2009, Lambert et al. 2010). In Finnish schizophrenia studies using a broad schizophrenia concept the rate of recovery ranges from 10 to 18% (Achté 1967, Lauronen et al. 2005) (Pauliina Juola 2015)
Before antipsykotics era in mid 50s coutcomes were good for 66% til 88% (Gottstein 2023). Bjornestad, Jone et al. 2017 found in "Antipsychotic treatment: experiences of fully recovered service users": "(b)etween 8.1 and 20% of service users with FEP achieve clinical recovery (Jaaskelainen et al. 2013)" with treatment as usual according to the standard guidelines. Recovery rates decreased: «17.7% in studies between 1941 and 1955, 16.9% in 1956–1975, 9.9% in 1976–1995, and 6.0% in studies after 1996» according to Jaaskelainen et al. 2013.
Why are Open Dialogues (2) spectacular good treatment results not of interest? Why is there no research to find out what the results are due to?
Neuroleptics (improperly called antipsychotics) were considered to be major advances in treatment. "Antipsychotic drugs revolutionized the care of schizophrenia, changing it from an incurable condition which required institutionalization to one that could be treated in the community, with the potential for independent living and recovery" concludes Professor Lawrie, as late as February 24, 2011 . NORMENT is based on its research: "Antipsychotic drugs are effective drugs for schizophrenia and have also been used in recent years for bipolar disorder."
In early episode schizophrenia research, the suggestion that postponing administration of antipsychotic medications may result in a poorer clinical course has raised the parallel ethical consideration of whether there is harm to subjects through “deferring neuroleptic treatment in first-episode patients while studies are conducted.” (John R Bola, 2005).
However, in a recovery perspective, it now appears that the treatment results (8.1 to 20% recovery) are very bad in the long term (3). Psychiatry seems to hold that current antipsychotics over-medication is effective in declaring schizophrenia as a chronic disease that requires lifelong medication.
One of the problems is the confirmation bias. It was easy for confirmations and conflicting information to be overlooked. Very simple is to see if the disease returns (recurrence) upon discontinuation of neuroleptics: " Reoccurrence of symptoms after discontinuation is an effect of discontinuation, not just an effect of the disorder." (Journal of the Norwegian Psychology Association , Vol. 52, No. 2, 2015 pages 126-131). This also applies to research: Bola et al. Cochrane.org 2011 found only 5 studies that were real placebo studies. One of these studies, Rappaport et al. 1978, found that unmedicated patients managed better, e. g. regarding readmission to hospital: NNH 2.9 (NNH = number nead to harm). The length of Follow-Up of this study was 3 years.
One was so convinced of the excellence of neuroleptics that there is no research comparing antipsychotics medication with psychosocial treatment or physical activity even though the effect of physical activity is documented (Gorczynski P, Faulkner, G 2010).
In spite of this research error which burdens the "placebo" group with withdrawal effects, the positive effects are small:
Reduction of at least 20–30% of psychotic symptoms are achieved according to Leucht et al 2009 effect of “(overall 41 versus 24% responded under SGA drugs and placebo, respectively) or an NNT of 6” i.e. for a small minority (1 in 6 patients) at the beginning of psychosis. Studies cover short-term and mid-term length. The Paulsrud committee found the same effects (1 in between 5 and 10 patients).
Leucht et al 2012 deals with maintenance treatment with neuroleptics. The studies range from 7 to 12 months. The results for preventing readmission are 1 in 5 patients (NNT = 5) and the conclusions for further research are "focus on outcomes of social participation and clarify the long-term morbidity and mortality." "Nothing is known about the effects of antipsychotic drugs compared to placebo after three years "(Leucht et al. 2012, p. 27).
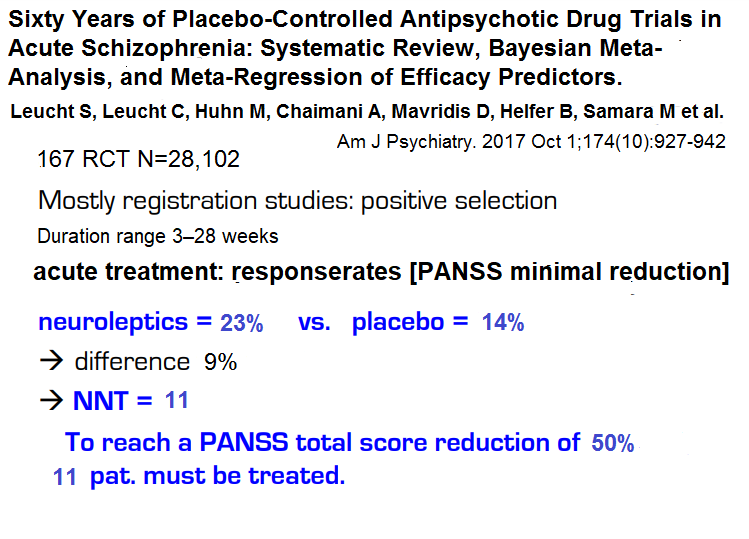
Leucht et al 2017 (“Sixty Years of Placebo-Controlled Antipsychotic Drug Trials in Acute Schizophrenia”) found "good response" for acute psychosis that 23% minus 14% placebo i.e. 9% for 50% or more reduction of symptoms PANSS. This effect is NNT=11. For 20% «minimal» symptom reduction the effect is 51% minus 30% placebo that equals 21% I. e. NNT=5.
[Nearly all Randomized Controlled Trials (RTC) use a “wash-out” period before randomizing to Placebo and drug because it was considered unethical not to give antipsychotics. Both Carpender and Bola found that studies with antipsychotica-naive participants are safe.
Dalsbø et al. 2019 concluded: “ It is uncertain if antipsychotics compared to placebo affects symptoms in persons with early psychosis” because antipsychotic-naive participants are missing.
Iversen et al. 2018 found in “Side effect burden of antipsychotic drugs in real life - Impact of gender and polypharmacy”: Use of antipsychotics showed significant associations to neurologic and sexual symptoms, sedation and weight gain, and >75% of antipsychotics-users reported side effects
Danborg et al. 2019 (Norwegian Institute of Public Health) concludes therefore: “The use of antipsychotics cannot be justified based on the evidence we currently have. Withdrawal effects in the placebo groups make existing placebo-controlled trials unreliable.”
The strict claim of antipsychotic-naive research leaves the medication of nearly all patients with diagnosis schizophrenia without justification and therefore maintenance results without relevance.
According to Norwegian law, forced drugging can only be used when, with “high probability, it can lead to recovery or significant improvement in the patient’s condition, or if the patient avoids a significant worsening of the disease.” Virtually all countries, apart from the United States, have ratified the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, which prohibits forced drugging, but the convention is up to now not followed.
In Norway, the Ombudsman concluded in December 2018, with reference to the Psychiatry Act, that it violated the law to use forced treatment with an antipsychotic in a concrete case. (Peter C. Gøtzsche, 2019). A study of the situation in Demark found that “Patients’ rights and the law were not being respected” (Gøtzsche et al. 2019).]
There is no evidence of maintenance treatment for more than 3 years Leucht et al. 2012 and FHI 2015: ISBN 978-82-8121-958-8. Bjornestad, Larsen et al. 2017 admits that evidence of maintenance medication is missing: "Due to the lacking long-term evidence base (Sohler et al. 2016) ..." Thus, positive effects for patients are not evidence-based after 3 years and the probability of evidence-based positive effects is strict taken zero.
Symptoms relief (12) and relapse prevention (Leucht et al 2012) are achieved only for a small minority in the beginning, RCT evidence beyond 3 years lacks completely and long-term use co-varies with more than approx. 40% reduction in recovery and approx. 40% increase in disability disability allowance/sickness (12). Nevertheless, psychiatry professors Jan Ivar Røssberg, Ole A. Andreassen, Stein Opjordsmoen Ilner (who educate psychiatrists) has a change-resistant, unrealistic and knowledge-resistant misrepresentation that antipsychotics contribute for "the vast majority contributing to the symptoms, functioning and higher self-reported quality of life. "(Doctors Journal, 12.05.2017). This delusion prevents the opening of drug-free treatment (3,4) in the psychosocial guidelines ("experimental, unethical", Larsen: "giant mistake", professional irresponsibility) and legitimises illegal forced medication. There is no evidence that antipsychotics promote "psychosocial functioning, professional functioning, and quality of life" (Buchanan et al 2009 PORT Treatment Recommendations). The county administration's practice regarding complaints against forced medication has been weakened by naive unscientific belief in psychiatrists' allegations and delusions. The county governor legitimises it by just giving 3% of the complaints pursuant and thus appears as a ridiculous appeal body (Ketil Lund). The Civil Ombudsman points out in law and order 05/2017 (Volume 56). Mental Health and Forced Medicine: "We are here in the core area of the principle of legality: Forced medication should not occur without the requirements of the law being met." Actually, "forced medication must be forbidden" (Ketil Lund). Dr. Peter Gøtzsche video: Forced Psychiatric Treatment Must be Abolished and Abolishing Forced Treatment in Psychiatry is an Ethical Imperative.
AFFIDAVIT OF PETER C. GØTZSCHE, MD about forced medication:
Conclusions
In my opinion, which is solidly based on scientific facts, administering a psychotropic medication or medications to a patient against his or her will is not in his or her best interest.
In my opinion, there are feasible less intrusive alternatives to administering a psychotropic medication or medications against a patient's will
Leslie Citrome 2011 gives («number needed to harm» (NNH)) for side-effect "Weight gain ≥7%", Somnolence and Akathisia for 10 different antipsychotics. The values differ for different drugs between NNH=6 for weight gain for Olansopine and 100 akathisia for Ziprasidone (see tabell).
"A meta-analysis by Allison and Casey 2008 provided an estimate of the mean weight gain in patients receiving standard doses of antipsychotics over a 10-week period: the mean increases were 4.45 kg with clozapine, 4.15 kg with olanzapine, 2.92 kg with sertindole, 2.10 kg with risperidone." Olanzapine with dose of 15mg/day may result in more than 10 kg the first year.
Iversen et al. 2018 concludes in “Side effect burden of antipsychotic drugs in real life - Impact of gender and polypharmacy”: Use of antipsychotics showed significant associations to neurologic and sexual symptoms, sedation and weight gain, and >75% of antipsychotics-users reported side effects. More side effects were observed in patients using several antipsychotics (p=0.002), with increasing total dose (p=0.021) and with antipsychotics in combinations with other psychotropic drugs. Patients and investigators evaluated the side effect burden differently, particularly related to severity, gender and antipsychotics dose.
Information brocheren of hospitals in Rheinland-Pfalz/Germany and Network Self-help on Mental Health in Rhineland Palatinate sponsored by the pharmaceutical industry gives bl. a. information on side effects:
1. Motor disturbances
•
cramping of the tongue and the muscles of the
throat, or visual
cramps (early dyskinesia; risk 2-25%)
•
limitations on movement, rigid gaze, trembling
(drug-induced
Parkinson syndrome; 15-30%)
• tortuous restlessness of the legs (akathisia; 20-25%)
•
permanent involuntary movement, especially
of the tongue, mouth or
facial muscles (tardive dyskinesia; 15-20%)
To sum up more patients (94%) suffer from side-effects than obtain symptom relief (9%).
OnwardMentalHealth.com mentions Risks & Limitations:
74% stop antipsychoyics due to poor risk/reward
77% with chronic psychosis don't have a good response
86% respond just as well to placebo as they do to antipsychitics
94% of people on antipsychoyics expierience side effects
Antipsychotics accelerate brain atrophy: the more are taken, the faster the brain shrinks
The > the number of antipsychotics taken together, the shorter life expectancy
3X risk of diabetes and large weight gain common on antipsychotics
2-3X lesslikely to be amployed if on antipsychotics long-term
2-5X less likely to recover on antipsychotics long-term
2X greater risk of cardiac death for the elderly on antipsychotics
Levine et al 2012 looked at treatment reactios for Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE). Ca. 73% became drop-outs. «Trajectory analysis of the entire sample identified that 18.9% of participants belonged to a group of responders. This figure increased to 31.5% for completers, and fell to 14.5% for dropouts.» For 72,9 % of drop-outs PANNS symptoms increased from ca. 3% in the beginning to 35% after 18 months. For 23,7% of completers PANNS symptoms increased from ca. 8% in the beginning to 30% after 18 months.
Koops et al. 2023: Addressing the Evidence to Practice Gap: What to Expect From International Antipsychotic Dose Reduction Studies in the Tapering Anti-Psychotics and Evaluating Recovery Consortium (TAPER): «Within the first year of treatment, up to 58% of patients discontinue medication without consulting their professional caregivers».
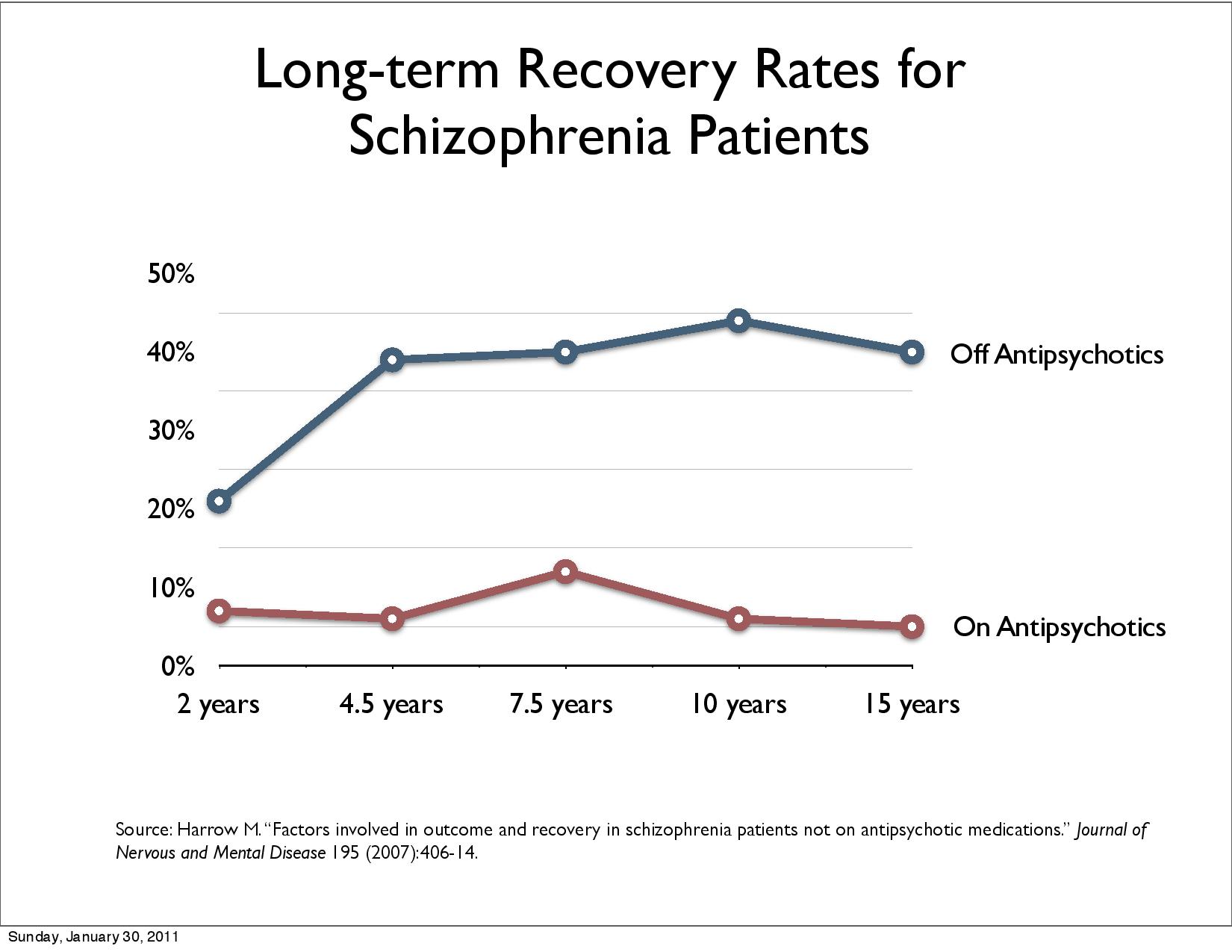
Harrow, M. & Jobe, T.H. (2012), Harrow et al 2014 (12) Long-term study shows that patients diagnosed with schizophrenia subject to drug-free treatment manage better in the long run, ie 50% significantly improved (higher recovery rate) after 15 years compared with 5%.
Wunderink randomized study replicated results. After 7 years, 40.4% recovery recovered and 17.6% with neuroleptics (12).
Harrow, M. & Jobe, T.H. (2017) concludes in "A 20-Year Multi-Followup longitudinal study assessing whether antipsychotic medications contribute to work functioning in schizophrenia":
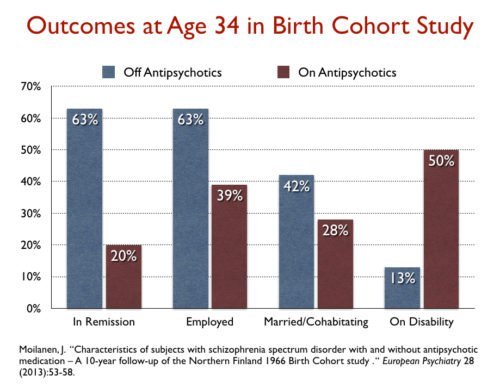
"Negative evidence on the long-term efficacy of antipsychotics has emerged from our own longitudinal studies and the longitudinal studies of Wunderink, of Moilanen, Jääskeläinena and colleagues using data from the Northern Finland Birth Cohort Study, by data from the Danish OPUS trials (Wils et al 2017) the study of Lincoln and Jung in Germany, and the studies of Bland in Canada, "(Among Bland RC and Orn H. (1978): 14-year outcome in early schizophrenia; Acta. Psychiatrica Scandinavica 58,327-338) the authors write. “These longitudinal studies have not shown positive effects for patients with schizophrenia prescribed antipsychotic for prolonged periods. In addition to the results indicating the rarity of periods of complete recovery for patients with schizophrenia prescribed antipsychotics for prolonged intervals, our research has indicated a significantly higher rate of periods of recovery for patients with schizophrenia who have gone off antipsychotics for prolonged intervals.” “The data indicate that any hypothesis based on the view that antipsychotics facilitate work functioning are extremely doubtful since the results for work functioning were running strongly (at significant levels) in the opposite direction.“
Harrow, M. & Jobe, T.H. (2018) :
Wunderink et al in the Netherlands, our own Chicago Followup Study, the Suffolk County study of Kotov et al in the US, and the long‐term data provided by the Danish OPUS trial, the AESOP‐10 study in England, the Finnish Birth Cohort Study, the Alberta Hospital Follow‐Up Study in Western Canada, and the international follow‐up study by Harrison et al are research programs included samples studied from 7 to 20 years. Unlike short‐term studies, none of them showed positive long‐term results.
Harrow, Jobe, Liping Tong (2021): Twenty-year effects of antipsychotics in schizophrenia and affective psychotic disorders:
“These and previous data indicate that after 2 years, antipsychotics no longer reduce psychotic symptoms and participants not on antipsychotic perform better.” Recovery Rate Six Times Higher For Those Who Stop Antipsychotics Within Two Years
Studies suggest that using minimal dose of neuroleptics for fewer patients over shorter time (Alvarez-Jimenez, Wunderink et al. 2016) is beneficial. «A Guide to Minimal Use of Neuroleptics: Why and How by Volkmar Aderhold, MD and Peter Stastny, MD, June 2015» shows the benefit of using minimal neuroleptics both low doses and fewer patients. "Brain changes through neuroleptics and therapeutic consequences" of Volkmar Aderhold shows changes in brain volume and possible consequences for treatment (5). Álvarez-Jiménez et al 2012 «provided support for the hypothesis that early functional and vocational recovery plays a pivotal role in preventing the development of chronic negative symptoms and disability. This underlines the need for interventions that specifically address early psychosocial recovery.» "Antipsychotics should be used more selectively, for shorter durations and with lowest possible effective dose." (Weinmann et al. 2010). Zhou Y, et al 2018: «Dose reduction of risperidone and olanzapine can improve cognitive function and negative symptoms in stable schizophrenic patients» [published online February 1, 2018].
Bola and Mosher 2003 compares Therapeutic Milieu vs Medications in the Hospital. Mean Effect Size (r) = 0.19 in favour of therapeutic milieu. Completing subjects had significantly better composite outcomes of a medium effect size at Soteria (+.47 SD, p =.03). Completing subjects with schizophrenia exhibited a large effect size benefit with Soteria treatment (+.81 SD, p =.02), particularly in domains of psychopathology, work, and social functioning. In addition, only 58% of Soteria subjects received antipsychotic medications during the follow-up period, and only 19% were continuously maintained on antipsychotic medications.
JR Bola et al. 2009: Psychosocial treatment, antipsychotic postponement, and low-dose medication strategies in first-episode psychosis: a review of the literature. «This review concluded that initial psychosocial treatment combined with time-limited postponement of antipsychotic medications may reduce long-term medication dependence and help to discriminate between similar (but pathophysiologically different) diagnostic entities for patients with early-episode schizophrenia.» Rappaport et al. 1978, Bola & Mosher 2003, Lehtinen et al. 2000 comprises ca. 40% til 60% patients psychosocial treatment and achieves pooled 17% effect size.
Jaakko Seikkula et al. 2010 (Journal Psychosis Volume 3, 2011 - Issue 3) found more than 80% recovery long-term effect for first-episode psychotic patients treated with Open Dialogue Therapy in Western Lapland (2, 5, 12): This shows the benefits of using not a lot of medications supported by psychosocial care. 19% were invalidated or sick after 5 years with 17% on neuroleptics (Scientific Symposium). With 75% on neuroleptics following the TAU guidelines, 62% were invalidated or ill after 5 years (12). This corresponds to approximately 40% increase in disability allowance/sickness. The incidence of psychosis was reduced from 33 to 2 per 100,000 inhabitants per year (5, 12).
Moritz S, et al. (2014) Sustained and "Sleeper" Effects of Group Metacognitive Training for Schizophrenia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. “All patients were prescribed antipsychotic medication....Metacognitive training demonstrated sustained effects in the reduction of delusions, which were over and above the effects of antipsychotic medication” (after 3 years).
Mössler K et al. 2011: Music therapy for people with schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders. «Music therapy added to standard care was superior to standard care for global state (medium-term, 1 RCT, n = 72, NNT 2 …). These effects seem to occur in a dose-effectiveness relationship (Gold et al., 2009; Gühne et al., 2012).
Amy M. N. Burns et al 2014: Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Medication-Resistant Psychosis: A Meta-Analytic Review. «Overall beneficial effects of CBT were found at posttreatment for positive symptoms (Hedges’ g=.47) and for general symptoms (Hedges’ g=.52)» (ca. NNT=3.6).
Til Wykes et al. 2008: Cognitive Behavior Therapy for Schizophrenia: Effect Sizes, Clinical Models, and Methodological Rigor. «Results: There were overall beneficial effects for the target symptom (33 studies; effect size=0.400...)» (NNT=4.5).
Pilling S et al. 2002: Psychological treatments in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis of family intervention and cognitive behaviour therapy. «Family intervention should be offered to people with schizophrenia who are in contact with carers. CBT may be useful for those with treatment resistant symptoms.»
Vocational rehabilitation for adults with psychotic disorders in a Scandinavian welfare society (Falkum et al. 2017): The total number of The Job Management Program, JUMP participants (CPT, CR) in any kind of vocational activity increased from 17 to 77% during the intervention. The total number of working participants in the TAU group increased from 15.5 to 18.2%.
Irene Bighelli et al., September 2018: Schizophrenia Psychological Interventions: Network Meta-Analysis of randomized evidence (SPIN-MA) «With 40 CBT studies, ... We found significant efficacy for CBT in comparison with treatment as usual in many outcomes (positive, overall and negative symptoms, response to treatment,quality of life and functioning), higher efficacy in comparison with inactive control for positive symptoms and response to treatment, and in comparison with supportive therapy for ad-herence...In conclusion, cognitive behavior therapy seems to be effective on positive symptoms in moderately ill patients with schizophrenia, with effect sizes in the lower to medium range (NNT 3.8), depending on the control condition.»
Irene Bighelli et al., December 2018: Response rates in patients with schizophrenia and positive symptoms receiving cognitive behavioural therapy. «Results We included 33 studies with a total of 1142 participants receiving cognitive behavioural therapy. On average, 44.5 and 13.2% of the patients reached a 20% (minimally improved) and 50% (much improved) reduction of overall symptoms. Similarly, 52.9 and 24.8% of the patients reached a 20%/50% reduction of positive symptoms.»
Agatha W.S.Wong et al. 2018: Group cognitive behavioural therapy for Chinese patients with psychotic disorder. «Nearly 61% of patients in the group CBTp showed at least 50% reduction on their score of delusion in the PSYRATS...Conclusion: Group CBTp can be an effective adjunctive psychological intervention in improving positive psychotic experiences among people with persistent psychotic symptoms, and can be applied in routine clinical practice.»
Cognitive therapy has shown effect for individuals diagnosed with “schizophrenia” and persistent psychotic symptoms who are taking neuroleptics (Wykes et al., 2008, Burns et al., 2014, Pilling et al., 2002, Danyael Lutgens et al. 2017). Peter C Gøtzsche et al. 2017: Cognitive behavioural therapy halves the risk of repeated suicide attempts.
A
positive therapeutic relationship, i.e. a “good therapeutic fit,“
seems to be the most salient factor for its effectiveness rather than
any specific psychotherapeutic method, as documented quite well by
Wampold
(2001).
Moritz
S, et al. (2014) Sustained and "Sleeper" Effects of
Group Metacognitive Training for Schizophrenia: A Randomized Clinical
Trial. “All patients were prescribed antipsychotic
medication...Metacognitive training demonstrated sustained effects in
the reduction of delusions, which were over and above the effects of
antipsychotic medication” (after 3 years).
John R Bola. 2005
(Medication-Free
Research in Early Episode Schizophrenia: Evidence of Long-Term Harm?)
found more than 4 studies showing positive effects of some weeks
medication free treatment after some years.
There is research that shows evidence for drug-free alternatives (4).
Rappaport et al. 1978 compares Hospital Milieu vs Medications in the Hospital. Mean Effect Size (r) = 0.18 in favour of hospital mileu. The 27% rehospitalization rate among placebo completers (11 of 41) is significantly lower than the 62% rate (34 of 39) among medication completers (r = −.32; study effect: r = −0.18). The length of Follow-Up of this study was 3 years.
Lehtinen et al. 2000 compares «Family Intervention vs Family Intervention plus Medications» Mean Effect Size (r) = 0.16 in favour of family intervention only.
Cullberg et al 2006. Treatment costs and clinical outcome for first episode schizophrenia patients: a 3-year follow-up of the Swedish "Parachute Project" and two comparison groups. «Symptomatic and functional outcome (need‐specific treatment) was significantly better compared with the Historical group and equal with the Prospective group.»
Effects of physical activity for diagnoses schizophrenia is documented by Gorczynski P, Faulkner, G 2010. «Two trials compared exercise to standard care and both found exercise to significantly improve negative symptoms of mental state (Mental Health Inventory Depression: 1RCT(randomised controlled trial), n=10, MD(medium diffenrence) 17.50, PANSS negative (symptoms): 1RCT, n=10, MD -8.50).).»
Fiona Pharoah et al., 2010: Family intervention for schizophrenia: «Family intervention may reduce the number of relapse events and hospitalisations and would therefore be of interest to people with schizophrenia, clinicians and policy makers.» (NNT 7).
Both Rathod et al 2010, Sarin et al 2011 and Swati et al 2011 show evidence of cognitive therapy for schizophrenia. Hutton P, Taylor PJ 2014 "Cognitive behavioral therapy for psychosis prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis" compares medicated and unedicated and finds that CBT is associated with a reduced risk of transition to psychosis.
Morrison et al. 2012 (9) concludes "A response rate analysis found that 35% and 50% of participants achieved at least a 50% reduction in PANSS (syptomer) total scores by than of therapy and follow-up respectively» this corresponds to NNT = 2 for « follow-up » with the aid of cognitive therapy, ie, only 2 patients must be treated for an additional patient to recover. With neuroleptics, it is 6 according to Leucht et al. 2009.
Francesca Bohn Vitzthum et al. 2014. Individualized metacognitive therapy program for patients with psychosis (MCT+): introduction of a novel approach for psychotic symptoms. “Conclusions: The present case history lends preliminary evidence for the feasibility of this new treatment approach in psychosis.”
Morrison et al. 2014 shows in "Cognitive therapy for people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders not taking antipsychotic drugs: a single-blind randomized controlled trial." “INTERPRETATION: Cognitive therapy significantly reduced psychiatric symptoms and seems to be a safe and acceptable alternative for people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders who have chosen not to take antipsychotic drugs.”
Jauhar et al. 2014 «Cognitive-behavioral therapy for the symptoms of schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis with examination of potential bias» shows therapeutic effect.
“Experiential Competence” writes April 28, 2014: "Psychotherapy for psychosis works" and refers to Michael Balter's "Talking Back to Madness" in the prestigious journal Science 14 Mar 2014: Vol. 343, Issue 6176, pp. 1190-1193. DOI: 10.1126 / science.343.6176.1190.
Ryan et al 2015. Metacognitive therapy (MCT+) in patients with psychosis not receiving antipsychotic medication: A case study. “Conclusions: The presented case studies provide preliminary evidence for the feasibility of MCT+ in treating patients not taking, or resistant to, antipsychotic medication.”
Jung, Esther, et al. 2016. Symptoms, functioning and coping strategies in individuals with schizophrenia spectrum disorders who do not take antipsychotic medication: a comparative interview study
Spectrum Disorders Fønhus MS, Fretheim A, Johansen M. has in "Drug-free Measures in Mental Health Protection" (Note from 2016. Oslo: Public Health Institute, 2016) found many drug-free treatments.
Eichner, C., & Berna, F. (2016). Acceptance and efficacy of metacognitive training (mct) on positive symptoms and delusions in patients with schizophrenia: A meta-analysis taking into account important moderators. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42(4), 952–962 viser evidens.
Liu, Y.-C., Tang, C.-C., Hung, T.-T., Tsai, P.-C., & Lin, M.-F. (2017). The efficacy of metacognitive training for delusions in patients with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials informs evidence-based practice. Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing. The MCT had a moderate immediate postintervention effect (g = -0.38)
Paul M. Grant et al., 2017, shows in the "Six-Month Follow-Up of Recovery-Oriented Cognitive Therapy (CT-R) for Low-Functioning Individuals With Schizophrenia" in a randomized study that "CT-R produced durable effects that were present even among individuals with the most chronic disease:» «(H)igher global functioning scores (between-group Cohen’s d=.53, i.e. approx. NNT=5.6), lower scores for negative symptoms (d=–.66, i.e.approx NNT=4.4), and lower scores for positive symptoms (d=–1.36, i.e. approx. NNT=2).”
David T Turner et al. 2017.A Meta-Analysis of Social Skills Training (SST) and Related Interventions for Psychosis. «SST demonstrated superiority over TAU (g = 0.3) ... Superiority was indicated in a proportion of comparisons for all symptoms pooled and social outcome measures.» (ca. NNT=6)
Fowler et al. 2018: Social recovery therapy in combination with early intervention services for enhancement of social recovery in patients with first-episode psychosis (SUPEREDEN3): a single-blind, randomised controlled trial.
Patrick McGorry et al. 2018: CAN SOME YOUNG PEOPLE RECOVER FROM FIRST-EPISODE PSYCHOSIS WITH INTEGRATED PSYCHOSOCIAL TREATMENT WITHOUT ANTIPSYCHOTIC MEDICATIONS? AN RCT TO ASSESS RISKS, BENEFITS, AND RANGE OF OUTCOMES. «The results of this study demonstrate that it is feasible and acceptable to conduct AP-free research in carefully selected FEP to examine the risk-benefit ratio of current treatments under carefully controlled conditions that prioritise patient outcomes and safety.»
Morrison et al 2018: «Antipsychotic drugs versus cognitive behavioural therapy versus a combination of both in people with psychosis: a randomised controlled pilot and feasibility study»: «A head-to-head clinical trial of CBT versus antipsychotics versus the combination of the two is feasible and safe in people with first-episode psychosis.»
Anthony P. Morrison 2018: Should people with psychosis be supported in choosing cognitive therapy as an alternative to antipsychotic medication?: A commentary on current evidence. Many patients choose not to take antipsychotic medication, often due to inefficacy or side effects, but there is little evidence regarding whether CBT can be effective as an alternative to antipsychotic medication. However, several recent trials suggest that CBT without medication may be a safe and acceptable option for people with psychosis.
Annbjørg Haram et al. 2018: Psychotherapy in schizophrenia: a retrospective controlled study. «At follow-up after a mean of 4 years and 1 month, the dialog therapy (DT) group had significantly higher scores on the GAF functions (GAF-F) and GAF symptoms (GAF-S) subscales compared to the standard psychiatric treatment (ST) group. Effect sizes (Cohen’s d) were very large, 238 for GAF-S and 241 for GAF-F.» Converted to NNT: NNT=1.35 (GAF-S) og NNT=1.35 (GAF-F) with conversion scheme https://rpsychologist.com/d3/cohend/
Jauhar et al. 2019: CBT for schizophrenia: a critical viewpoint. «CBT was originally introduced to treat the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, but its effect on these, according to convergent meta-analytic evidence, is small.»
Annbjørg Haram et al. 2019: Impact of Psychotherapy in Psychosis: A Retrospective Case Control Study. Results: At follow-up, GAF functioning (GAF-F) and GAF symptom (GAF-S) scores both were significantly higher in the DT group than the ST group. Effect sizes (Cohen's d) were large; 1.8 for GAF-S (NNT=1,6) and 2.1 for GAF-F (NNT=1,4).
Daniela Polese et al. 2019: Treatment-Resistant to Antipsychotics: A Resistance to Everything? Psychotherapy in Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia and Nonaffective Psychosis: A 25-Year Systematic Review and Exploratory Meta-Analysis. «Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) was the most frequently recommended psychotherapy intervention for TRS (studies, n = 32, 76.2%), showing efficacy for general psychopathology and positive symptoms as documented by most of the studies. CBT, psychosocial intervention, supportive counseling, psychodynamic psychotherapy, and other psychological interventions can be recommended for clinical practice.»
Anthony Morrison April 2019: COGNITIVE BEHAVIOUR THERAPY FOR PEOPLE WITH PSYCHOSIS. «This trial demonstrated that CBT resulted in a significant improvement in overall symptoms at end of treatment (9 months) in comparison to treatment as usual, but that this benefit was not maintained at long-term follow-up (21 months).»
Francey et al. 2020: Psychosocial Intervention with or without Antipsychotic Medication for First Episode Psychosis: A Randomized Noninferiority Clinical Trial. «The primary outcome was level of functioning as assessed by the SOFAS at 6 months... The selected sample recruited to this study, psychosocial treatment alone was not inferior to psychosocial treatment plus antipsychotic medication»
Bighellei et al. 2021: Psychosocial and psychological interventions for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. «We found robust benefits in reducing the risk of relapse for family interventions, family psychoeducation, and cognitive behavioral therapy. These treatments should be the first psychosocial interventions to be considered in the long-term treatment for patients with schizophrenia.»
Bighelli et al. 2022: Effects of psychological treatments on functioning in people with Schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. «We found that psychological interventions overall showed a benefit in improving functioning compared to control conditions. According to Cohen this effect is small to medium»
This illustrates Klingberg's point (2012) that cognitive therapy has no evidence problem but an implementation problem (4, 10).
Professor, Dr. Med. Peter C. Gøtzsche supports medicine-free treatment. Robert Whitaker looked 2016 at “Recovery Rates and Long-term Outcomes for Unmedicated Patients with Schizophrenia.” The findings where promising.
In addition to the Open Dialogue (2), there are several other alternatives to TAU (Treatment as usual): Recovery-Oriented Cognitive Therapy (CT-R), SOTERIA APPROACH, HEARING VOICES APPROACH, HARM REDUCTION APPROACH (Will Hall), SHARED DECISION MAKING (Deegan, 2007; Deegan & Drake, 2007; Roe & Swarbrick, 2007) (15).
In the mid-50s antipsychotics / neuroleptics where introduced. In the 3 decades from 1950s to 1980s inpatient suicides in psychiatric hospitals ten doubled in Norway (Retterstøl 1988), raised from 50 to 400 per 100 000 in V.A. Hospitals ( Farberow 1975). Similar tendencies are reported from more that 8 countries (Chart 1: Bowers et al. 2008).
Life expectancy for psychiatric patients in the 2000s was reduced even more.
“SMRs for the 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s were 1.8, 3.0, and 3.2, respectively” (John McGrath et al. 2008) i.e. mortality rates continue to increase in several countries. “The most striking figure in this study is that eliminating suicide in schizophrenia would restore life expectancy to normal.” (David Healy et al 2012). Tiihonens 2009 FIN11 cohort study suggested that antipsychotic use decreased all-cause mortality. De Hert et al. 2010 showed incomplete reporting of data e. g. “exclusion of deaths occurring during hospitalization leading to exclusion of 64% of deaths on current antipsychotics from the analysis”.
Reduced lifetime expectancy for male psychiatric patients in the 21st century was 22 years in Denmark, 19 years in Finland and 20 years in Sweden. This corresponded to the SMR for life expectancy of 2.5 for Denmark, 1.8 for Finland and 2.2 for Sweden, respectively. SMR for suicide was 25, 9 and 21, i.e. suicide is the dominant cause. Women's numbers are lower (Wahlbeck et al 2011).
Ray et al 2009 «Atypical antipsychotic drugs and the risk of sudden cardiac death.» finds: «For both classes of drugs, the risk for current users increased significantly with an increasing dose. Among users of typical antipsychotic drugs, the incidence-rate ratios increased from 1.31 for those taking low doses to 2.42 for those taking high doses.» Therefore "Antipsychotics should be used more selectively, for shorter durations and with lowest possible effective dose." (Weinmann et al. 2010).
Diagnosis has long tradition, but there has been met with increasing criticism. Rosenhahn experiment showed that psychiatric diagnosis is not reliable. Professor Sami Timimi has looked if there is evidence that diagnosis hjelps. The result was that diagnosis should be abandoned because there is not sufficient evidence that it helps. Lucy Johnstone 2017 develops alternatives.
Europe's mental health institutions uniformly substandard, says WHO. None of the 75 sites visited by experts met the standards of care set by the United Nations.
Only little effect of symptom reduction in the beginning (Leucht et al 2009), no evidence for effect after three years (Leucht et al 2012), no evidence for promotion of recovery (Buchanan et al 2009 PORT Treatment Recommendations) and the excellent recovery results (Seikkula 2014) of Open dialogue with 83% unmedicated long-term (5, Seikkula 2016) have raised the question if antipsychotics do more harm then good in the long term.
What is the possible harm?
A chronicity problem with antipsychotic drugs became apparent in the 1960s and 1979s, e.g. Schooler 1967, Prien 1968, Prien 1971, Bockoven 1975, Carpenter 1977, Rappaport 1978, Soteria Project (Mathews 1979, Mosher 1978 and 1995, Bola 2003), Cole 1977 (17), MCWALTER et al. 1961 and has continued to show up in outcome studies ever since: WHO studies (Leff 1992), (Jablensky 1992), Vermont study (Harding 1987), Harding 1990, Hagerty 1994 and Harrow 2007.
A biological explanation is hypersensitivity caused by neuroleptics: Muller, P 1978, Chouinard, G 1978, Chouinard, G 1980, Chouinard, G 1982, Seeman, P. 2005 og Samaha, A. 2007.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) studies show «brain shrinkage»: Chakos, M. 1994, Madsen, A. The Lancet 32 (1998), Gur, R. 1998, Gur, R. Archives of General Psychiatry 55 (1998), Ho, B. Arch Gen Psych 60 (2003), Ho, B. Arch Gen Psych 68 (2011), Antonio Vita et al. 2015.
P. Fusar-Poli et al. 2013: Progressive brain changes in schizophrenia related to antipsychotic treatment? A meta-analysis of longitudinal MRI studies. “The gray matter volumes (GMV) decreases were inversely correlated with cumulative exposure to antipsychotic treatments, while no effects were observed for duration of illness or illness severity.”
Veijola et al. 2014 “Longitudinal changes in total brain volume in schizophrenia: relation to ...antipsychotic medication.” finds “The mean annual whole brain volume reduction was 0.69% in schizophrenia, and 0.49% in controls” by regression.
van Erp et al 2018: Cortical Brain Abnormalities... Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics Through Meta Analysis (ENIGMA) Consortium «higher medication doses “were significantly correlated with thinner cortex in almost all” regions of the brain»
Tardive dyskinesia and global decline: Crane, G. 1968, Crane, G. Science 181 (1973), Yassa, R. 1989, Myslobodsky, M. Brain and Cognition 23 (1993), Waddington, J. 1993, De Leon, J. 2007, Harrison, P. 1999.
There have been questions about increased drug use of neuroleptics and antidepressants and increased disability benefits have a connection. Award-winning science writer Robert Whitaker wrote: Causation, Not Just Correlation: Increased Disability in the Age of Prozac (6). Robert Whitaker reviewed already 2010 in Anatomy of an Epidemic the scientific literature to investigate the long-term effects of psychiatric medications, which showed the damage of todays overmedication.
Clare Parish found that brain volume shrinks ("Antipsychotic deflates the brain") also see Andersen et al. The reduction in brain volume due to prolonged "antipsychotic" use reduces cognitive abilities (PLOS Medicine: Antipsychotic Maintenance Treatment: Time to Rethink? Joanna Moncrieff. Published: August 4, 2015). Theo G.M. van Erp et al 2018 conducted “the first meta-analysis of cortical thickness and surface area abnormalities”. Husa et al. 2017 finds for patients diagnosed schizophrenia: «Higher lifetime antipsychotic dose-years were significantly associated with poorer cognitive composite score at age 43 years».
Psychiatric patients have approx. 25 years shorter life. Recent research recommends reduced long-term use of antipsychotics to increase life expectancy for patients (Athif Ilyas et al, 2017). PETER C. GØTZSCHE, Professor, Dr. Med., Rigshospitalet Copenhagen writes "(T)o sum up, psychotropic drugs are the third most common cause of death in Western countries after cardiovascular disease and cancer." (7). In 'Deadly psychiatry and organized denial' (2015) P. Gøtzsche writes: "we could reduce our current usage of psychotropic drugs by 98% and at the same time improve patients' mental and physical health and survival"(8). Professor Peter C Gøtzsche concludes 10. January 2018 «Psychiatry is a disaster area in healthcare that we need to focus on» (BMJ 2018;360:k9).
It appears that recovery in the longer term was better before neuroleptics were introduced (8). The national guidelines to treat psychosis in Norway refer to recovery. However an additional 5 years of long-term medication is proposed in the case of relapse after 2 years. Leucht et al. 2009 with symptom relieve for 1 in 6 patients is included in the reference list. Nevertheless, it is stated that "50-80% of patients who receive effective medicine will be significantly better" on the basis of outdated studies from the 1990s and that the placebo effect seems to be added. Therefore all diagnosed schizophrenia are offered drugs. The result is that TIPS prosject medicated all, Svedberg et al. 2001 93%, and in Australia more then 90% tok psykotropic medicine (Waterreus et al., 2012).
From an evidence-based point of view, the current practice of long-term medication is an experimental, unethical chance game that is incorrect. Experience and cohort studies show that long-term recovery is seriously impaired. Here the doctor's principle is touched "first, do no harm." It is encouraged that over-medication practice is terminated in favour of evidence-based health promotion practices that take care of recovery opportunities, i.e. the health of the patients (12).
AFFIDAVIT OF Robert Whitaker 1. June 2016:
In summary, the research literature reveals the following:
a) Antipsychotics increase the likelihood that a person will become chronically ill.
b) Long-term recovery rates are much higher for unmedicated patients than for those who are maintained on antipsychotic drugs.
c) Antipsychotics cause a host of debilitating physical, emotional and cognitive side effects, and lead to early death.
d) The new “atypical” antipsychotics are not better than the old ones in terms of their safety and tolerability, and quality of life may even be worse on the new drugs than on the old ones.
Peter C Gøtzsche concludes 10 January 2018 (BMJ 2018;360:k9): «Psychiatry is a disaster area in healthcare that we need to focus on» (16):
Firstly, the effects of psychiatric drugs are not specific.
Secondly, the research in support of the paradigm is flawed
Thirdly, the widespread use of psychiatric drugs has been harmful for the patients.
Fourthly, all attempts at showing that psychiatric disorders cause brain damage that can be seen on brain scans have failed.
There are four main problems with psychiatric drug trials:
Almost all placebo-controlled trials are flawed due to their cold turkey design
The trials are insufficiently blinded
Psychiatrists assess the effect using rating scales, the relevance of which for the patients is often uncertain
Selective reporting of outcomes is very common and can be very serious
Psychiatry needs a revolution. Reforms are not enough. We need to focus on psychotherapy and to hardly use any psychiatric drugs at all.
Rindal, 10. January
2018 [update]
--
--
Walter Keim
Netizen:
http://walter.keim.googlepages.com
Paradigm shift: Open dialogue reduces schizophrenia per year to
one tenth and quadruples recovery (from less then 20% to 80%)
http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/recovery-en.html
[Follow-up:
Tomi Bergström, Jaakko Seikkula et al. 2018: The family-oriented open dialogue approach in the treatment of first-episode psychosis: Nineteen–year outcomes. Psychiatry Research Volume 270, December 2018, Pages 168-175
Pat Bracken. Beyond Models, Beyond Paradigms. The Radical Interpretation of Recovery http://www.peter-lehmann-publishing.com/articles/others/pdf/bracken_recovery.pdf
Economic consequence: In the year 2012 there where « 8399 individuals with schizophrenia» in Norway. Total cost was USD 890413045.- (Prevalence, Employment Rate, and Cost of Schizophrenia in a High-Income Welfare Society: A Population-Based Study Using Comprehensive Health and Welfare Registers. October 2015 Schizophrenia Bulletin DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbv141). Would cutting down medication to half cut in half costs and reduce sufferings of patients?]
Reference:
Robert Whitaker - March 25, 2017. The Door to a Revolution in Psychiatry Cracks Open. A MIA Report: Norway's Health Ministry Orders Medication-Free Treatmen https://www.madinamerica.com/2017/03/the-door-to-a-revolution-in-psychiatry-cracks-open/
Jaakko Seikkula - 7 Principles of Open Dialogue - DK 3 - Roskilde- August 29, 2014: 3. http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/Seikkula2014.pdf
Knowledge- and research-based liquidation of current harmful psychiatric medication in favour of evidence-based practice to promote recovery http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/open_letter_knowledge.html
Sami Timimi. Tidsskr Nor Legeforen 2017 137:421 DOI: 10.4045/tidsskr.17.0240 The option of drug-free/drug withdrawal is the minimum that all http://tidsskriftet.no/2017/04/kommentar/option-drug-freedrug-withdrawal-minimum-all
Scientific Symposium. Pharmaceuticals – risks and alternatives. The 15th of October 2016 in Gothenburg, Sweden. Jaakko Seikkula, Professor of Psychotherapy, Clinical Psychologist, Finland. Naturalistic study designs for developing the system to reduced medication http://extendedroom.org/en/scientific-symposium/
Robert Whitaker: Causation, Not Just Correlation: Increased Disability in the Age of Prozac: https://www.madinamerica.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Causation-not-just-correlation-.pdf
Professor, Doctor of Medical Science, Peter C. Gøtzsche The third leading cause of death after heart disease and cancer?: http://cepuk.org/2015/05/13/third-leading-cause-death-heart-disease-cancer-experts-debate-harmful-effects-psychiatric-medications/ (in Danish: http://www.deadlymedicines.dk/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Diagnoser_kap-7.pdf
Professor PETER C. GØTZSCHE: Deadly Psychiatry and Organised Denial (pdf). https://www.amazon.com/Deadly-Psychiatry-Organised-Denial-Gotzsche-ebook/dp/B014SO7GHS
Morrison AP, Hutton P, Wardle M et al.
Psychological Medicine. Volume 42, Issue 5 May 2012, pp.
1049-1056. Cognitive
therapy for people with a schizophrenia spectrum diagnosis not
taking antipsychotic medication:
an exploratory trial. Psychol Med 2012; 42: 1049 – 56
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21914252?dopt=Abstract
P.Hutton et al. 2013: Cognitive behavioural therapy for psychosis prevention: A systematic review and meta-analysis: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236073727_Cognitive_behavioural_therapy_for_psychosis_prevention_A_systematic_review_and_meta-analysis
Hutton P, Taylor PJ 2014 «Cognitive behavioural therapy for psychosis prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis» sammenlikner medisinerte og umedisinerte og finner at CBT er forbundet med nedsatt risiko for overgang til psykose.
Klingberg S, Wittorf A. Evidencebased psychotherapy for
schizophrenic psychosis. Nervenarzt 2012; 83:
907-918.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22733380
Robert Whitaker, February 2017: Rethinking Antipsychotics Recovery Rates and Long-term Outcomes for Unmedicated Patients with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders (pdf)
Is it possible to give a rough guess on the
long-term effect/harm of antipsychotics on
recovery?
http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/question-recovery.html
Peter C. Gøtzsche. Professor, dr.med. Det Nordiske Cochrane Center Rigshospitalet, København: «Medicinfri psykiatri er veldokumenteret og tvangsmedicinering skal afskaffes» http://www.deadlymedicines.dk/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Gøtzsche-til-Tidsskriftet-om-medicinfri-psykiatri.pdf
Peter C. Gøtzsche. Professor, dr.med. Medicinfri psykiatri. Tidsskrift for Den norske legeforening. https://tidsskriftet.no/2017/05/kommentar/medicinfri-psykiatri
A Critical Literature Review of the Direct, Adverse Effects of Neuroleptics (also known as antipsychotics). Essential Information for Mental Health Consumers, Carers, Families, Supporters and Clinicians: https://nmhccf.org.au/sites/default/files/docs/nmhccf_-_clr_-_web_accessible_version_-_final_-_august_2017_0.pdf
Peter C Gøtzsche 10 January 2018 Psychiatry is a disaster area in healthcare that we need to focus on (BMJ 2018;360:k9) http://www.bmj.com/content/360/bmj.k9/rr-15
Robert Whitaker 2015: Antipsychotics/Schizophrenia: Antipsychotic Drugs and Chronic Illness. A. The Chronicity Problem Becomes Apparent (1960s-1970s) https://www.madinamerica.com/mia-manual/antipsychoticsschizophrenia/
Tomi Bergström, Jaakko Seikkula et al. 2018: The family-oriented open dialogue approach in the treatment of first-episode psychosis: Nineteen–year outcomes. Psychiatry Research Volume 270, December 2018, Pages 168-175: https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1XmgRbZg70VfA

Results of long-term use of antipsychotic drugs: