and mail this URL to your friends!
|
and mail this URL to your friends! |
Mainly in Scandinavia, English Speaking countries and German speaking countries.
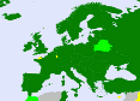
 Freedom
of Information - also known as access to information (ATI), the
public's right to know or administrative transparency - gives
citizens access to official information hold by government and other
public authorities. In 1766 a Freedom
of Information Law (Tryckfrihetsförordningen) was introduced in
Sweden-Finland,
thanks to a Finn
named Anders
Chydenius,
who faught for democracy, equality, and respect for the human rights.
1888 followed Columbia, 1951 Finland
(independent
1917) and 1966 the USA.
Freedom
of Information - also known as access to information (ATI), the
public's right to know or administrative transparency - gives
citizens access to official information hold by government and other
public authorities. In 1766 a Freedom
of Information Law (Tryckfrihetsförordningen) was introduced in
Sweden-Finland,
thanks to a Finn
named Anders
Chydenius,
who faught for democracy, equality, and respect for the human rights.
1888 followed Columbia, 1951 Finland
(independent
1917) and 1966 the USA.
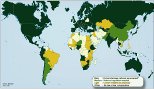
Since then more than 100 countries adopted such laws. Many countries guarantee FOI in constitutions. More thens 125 states with more then 5.9 billion inhabitants adopted FOI laws or provisions in constitutions. ATI is now firmly recognised as an internationally guaranteed human right, with decisions at the Inter-American Court of Human Rights and European Court of Human Rights, and global recognition by the UN Human Rights Committee. All countries in Europe have FOI laws or are preparing bills. Nearly all OECD countries and all developed countries recognize Freedom of information. Right2Info.org gives an overview. Transparency was the Word of the Year 2003. The EU Charter of Fundamental Rights gives in Article 42 a right of access to documents of the European Parliament, Council and Commission.
The International Symposium "Freedom of Information and Data Protection in the Enlarged European Union" shows that maybe Germany would have to adapt FOI first to get goodwill, if it would apply to the EU today. The "European Parliament resolution on the situation as regards fundamental rights in the European Union (2000) (2000/2231(INI))" document A5-0223/2001 "notes ... that both the EU institutions and the Member States uphold the rights set out in the various Chapters of the EU Charter"
 On
the lists above you find FOI laws of
On
the lists above you find FOI laws of
Scandinavian countries (Sweden (1766), Finland, Norway, Denmark und Island),
English speaking countries USA (1966), Ireland, England (UK) and
German speaking countries Austria (1987), Switzerland (2004?) and Germany (in federation, 2005).
Other members of EU: France (1979), Greece (1986), Austria (1987), the Netherlands (1991), Belgium (1991), and since some years Italy (1990), Spain (1992), Portugal (1993), Ireland, Malta, (1997) Luxemburg (2018), Cyprus (2017) and many
central and eastern European states like Hungary (1992), Ukraine (1992, Law No. 2657-XII), Russia (1995, Act No. 24-FZ), Uzbekistan (1997), Latvia (1998), Georgia (1998), the Czech Republic (1999), Albania (Law No. 8503, 1999), Bulgaria (2000), Bosnia (2000), Estonia (2000), Lithuania (2000), Slovakia (2000), Moldova (2000), Poland (2001), Romania (2001), Armenia (2003), Slovenia (2003) and Turkey (2003), Croatia (2003), Kosovo (2003), Switzerland (2004) and Yugoslavia (Serbia 2004), Montenegro (2005), Azerbaijan (2005) and Macedonia (2006) .
Germany is in 5 of 16 states nearly the only major country in Europe without Freedom of Information. In Cyprus access to information rights are part of the constitution. Here is a detailed survey of Christoph Sobotta for European states.
Article 42 of the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights and Article 255 of the Treaty are implemented by Regulation (EC) No 1049/2001 for the European Parliament, Council and Commission. A selection of legal texts concerning public access to documents including case law.
|
Organisation |
Name with Link |
Translation |
|
Universal Declaration of Human Rights: Article 19: ...Freedom to seek information" |
||
|
United Nations, 1966 |
International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.(ICCPR) (BGBl. 1973 II S. 1534) Article 19 (2) Freedom to seek information" |
|
|
Europe UNECE, 1998 |
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe: Environmental Matters: The Aarhus Convention: http://www.unece.org/env/pp/acig.htm |
|
|
COMMISSION ON HUMAN RIGHTS, 1998 |
E/CN.4/1998/40, 28 January 1998: Promotion and protection of the right to freedom of opinion and expression Report of the Special Rapporteur, Mr. Abid Hussain, submitted pursuant to Commission on Human Rights resolution 1997/26: III A |
|
|
UN Special Rapporteur, 1999 |
JOINT
DECLARATION |
|
|
COMMISSION ON HUMAN RIGHTS, 2000 |
E/CN.4/2000/63, 18 January 2000: Report of the Special Rapporteur on the promotion and protection of the right to freedom of opinion and expression, Mr. Abid Hussain, submitted in accordance with Commission resolution 1999/36: III B |
|
|
UN, OAS Special Rapporteurs, OSCE Representative, 2004 |
JOINT DECLARATION by the UN Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Opinion and Expression, the OSCE Representative on Freedom of the Media and the OAS Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Expression: http://merlin.obs.coe.int/iris/2005/2/article1 "The right to access information held by public authorities is a fundamental human right" |
|
|
German government 11 Feb. 2011 |
Germany tried to remove the human right of access to public documents and other human rights from the Draft General Comment No. 34 on Article 19 ICCPR (see page 17 of the notes of the meeting of the Human Rights Committee 18 MARCH – 24 MARCH 2011). |
|
|
Tenth Joint Declaration by the Four Special International Mandates for Protecting Freedom of Expression, 3. February 2010 |
Although great strides have been made over the last decade in recognising the right to information, the fourth challenge recognises that much still remains to be done... Many laws that have been passed fail to meet minimum international standards, and implementation efforts remain too weak in many countries: http://merlin.obs.coe.int/iris/2010/5/article1 |
|
|
General Comment No. 34 on Article 19 of the ICCPR, 21. July 2010 |
Human Rights Committee - General Comment No. 34: "18. Article 19, paragraph 2 embraces a general right of access to information held by public bodies. Such information includes all records held by a public body...": http://www2.ohchr.org/english/bodies/hrc/comments.htm |
|
|
UN. ACHPR, OAS Special Rapporteurs, OSCE Representative, 12 June 2013 |
GLOBAL PRINCIPLES ON NATIONAL SECURITY AND THE RIGHT TO INFORMATION (“THE TSHWANE PRINCIPLES”) |
German |
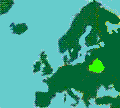 Freedom
of Information came 1766
to Sweden, 1951
to Finland, 1966
to den USA, 1970 to Norway
and 1985
to Denmark In 1981 the Council of Europe gave "Recommendation
No. R (81) 19" on the access to information held by public
authorities. A new Recommendation
Rec(2002)2 was adopted 2002. Both EU and nearly all countries in
the EU and Europe adopted such laws. However citizen rights vary and
there are no minimum standards. In order to keep up with the
international development freedom of information should be
strengthened in EU member states. Here is a petition
to the European Parliament.
Freedom
of Information came 1766
to Sweden, 1951
to Finland, 1966
to den USA, 1970 to Norway
and 1985
to Denmark In 1981 the Council of Europe gave "Recommendation
No. R (81) 19" on the access to information held by public
authorities. A new Recommendation
Rec(2002)2 was adopted 2002. Both EU and nearly all countries in
the EU and Europe adopted such laws. However citizen rights vary and
there are no minimum standards. In order to keep up with the
international development freedom of information should be
strengthened in EU member states. Here is a petition
to the European Parliament.
Support Freedom of Information, by
the following call of Statewatch (click here):
I/We
support the call to EU institutions for a democratic and accountable
"Open Europe" on access to documents.
Freedom of Information came 1766
(1949) to Sweden, 1951
to Finland, 1966
to den USA, 1970 to Norway
and 1985
to Denmark. In 1981 the Council of Europe gave "Recommendation
No. R (81) 19" on the access to information held by public
authorities. Germany is the only country in the EU without such a
law. In order to keep up with the international development freedom
of information should also be adopted in Germany.
Support
the German Freedom of Information Law, by
the following E-Mail to the German Government (click here):
I
support the call to the German Government for a democratic and
accountable Freedom of Information Law on access to public
documents.
(You
may change the text according to your needs).

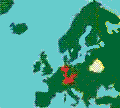 The
Federal Republic of Germany is nearly the only country in the EU
without FOI. But 11 of 16 federal federal states (Bundesländer)
Brandenburg,
Berlin,
Schleswig-Holstein,
North
Rhine-Westphalia, Mecklenburg-Western
Pomerania, Bremen,
Saarland, Hamburg, Thuringia
and Rheinland-Pfalz
have adopted FOI laws. Opposition parties in the states of
Bavaria, Hesse, Lower
Saxony, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt
have suggested FOI laws. Unfortunately parliaments in
Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony and Saxony have
voted against FOI laws.
The
Federal Republic of Germany is nearly the only country in the EU
without FOI. But 11 of 16 federal federal states (Bundesländer)
Brandenburg,
Berlin,
Schleswig-Holstein,
North
Rhine-Westphalia, Mecklenburg-Western
Pomerania, Bremen,
Saarland, Hamburg, Thuringia
and Rheinland-Pfalz
have adopted FOI laws. Opposition parties in the states of
Bavaria, Hesse, Lower
Saxony, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt
have suggested FOI laws. Unfortunately parliaments in
Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony and Saxony have
voted against FOI laws.
Support the Freedom of Information laws in
the states of: Baden-Württemberg,
Bavaria,
Hesse,
Lower
Saxony, Saxony
with the following E-Mail:
I
support the call to the German Federal State (Bundesland)
Government for a democratic and accountable Freedom of Information
Law on access to public documents.
(This E-Mails is send to the parties governing
the state, with a copy to the opposition suggesting the FOI law. You
may change the text according to your needs).
Warning: I do not accept any liability that the information on these pages is correct, accurate or up to date!
Please feel free to link this site!
Thanks to all, who gave me this information. Please do not hesitate to mail me if you have additional information.
Visitor No.
since 25. July 2001
[Back to page on Freedom of Information] [Petitions] [Patients Rights in Europe] [Violations of Human Rights] [Back to Homepage]