Human Right Violations in Germany: Freedom of Opinion, Information,
Association, Family Life and Right to Fair Trial
On December 10, 1948 the General Assembly of the United Nations adopted
and proclaimed the Universal
Declaration of Human Rights. Afterwards many binding international
conventions were signed to secure human rights. Germany has among other
signed the following conventions:
The European Union guarantees Human Rights according to Article 53 of the
Charter
of
Fundamental Rights of the EU and Article
6
(1) of OF THE TREATY ON EUROPEAN UNION.
Violations of the ECHRFF
can be reported to the European Court
of Human Rights. The Human
Rights
Committee
of the UN is responsible for complaints about the ICCPR.
Human rights in question are:
Access to information is now firmly recognised as an internationally
guaranteed human right, with decisions at the Inter-American Court of
Human Rights and European Court of Human Rights, and global recognition by
the UN Human Rights Committee. The European Court of Human Rights
ruled 14. April 2009 in application no. 37374/05
by TÁRSASÁG A SZABADSÁGJOGOKÉRT ./. Hungary that access to public
documents to be a human right according to Article 10 of the ECHRFF.
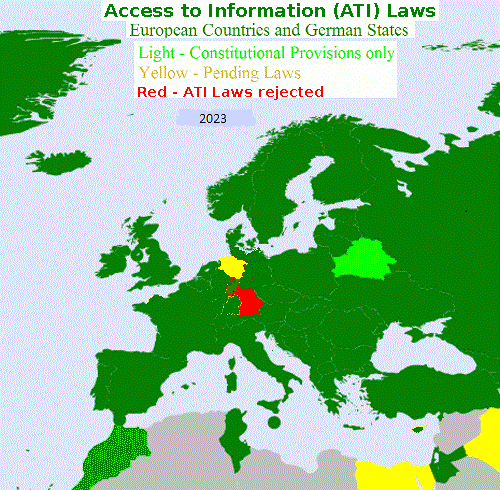
In 5 German federal states Bavaria,
Baden-Württemberg, Hesse, Lower Saxony and Saxony access to information
laws are missing. 125
states with 5.9 billion inhabitants
adopted either FOI laws or constitutional provisions. Citizens in 5 states
with half of the population in Germany lack this human right.
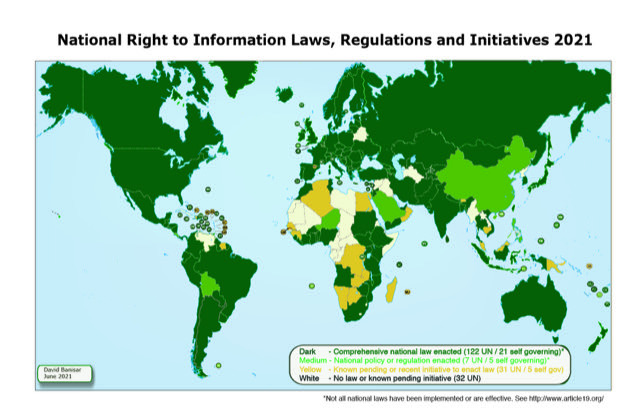
The federal law of Freedom of Information has too many exeptions and
violates international principle of maximum disclosure. Comparison with
laws from 111 other counntries places Germany
on 105th rank, i. e. 5.5 billion people have better access laws.
Germany tried to remove the human right of access to public documents and
other human rights (Appendix
25) from the Draft
General
Comment No. 34 on Article 19 ICCPR (see page 17 appendix
26).
The Human Rights
Council supported 6 of 8 suggestions of the Baltic Sea NGO Forum.
The following cases about violation of human rights are known to me:
- In complaint No. 40901/02 to the European Court of Human Rights 1 of 13.
November 2002 violations of freedom of opinion have been filed. This
case is because a integration helper violated
2 the law on legal advice 16. for supporting
Jewish immigrants for free. Germany is the only country in the world where it is
forbidden to altruistically give free legal advice.
- In case BARTHOLD v. GERMANY and STAMBUK v. GERMANY freedom
of opinion was violated.
- In case Vogt vs. Germany ( - 7/1994/454/535 - EuGRZ 1995, 590 - ) 3 , Germany was condemned because of violations of
freedom of opinion and freedom of association by the European Court of
Human Rights. But the German courts seem not to respect this judgement 4 and try to continue as before: new cases in 2004.
- Unfair trials (Violation of
Article 6 of the ECHRFF 14 ): Deumeland v. Germany,
BOCK v. GERMANY , PAMMEL v. GERMANY , PROBSTMEIER v. GERMANY , KÖNIG v. GERMANY , ELSHOLZ v. GERMANY , SOMMERFELD v. GERMANY , KLEIN
v. GERMANY , MIANOWICZ v. GERMANY , METZGER v. GERMANY , H.T. v. GERMANY , HOFFMANN v. GERMANY , P.S. v. GERMANY , JANSSEN v. GERMANY , KIND v. Germany, BECKER v. GERMANY , BÖHMER v. GERMANY, THIEME v. GERMANY , HASSE-ANGER v. GERMANY , NIEDERBOSTER v. GERMANY, VAN KUCK v. GERMANY, HERBOLZHEIMER v. GERMANY, GÖRGÜLÜ v. GERMANY, Storck v. Germany, SÜRMELI / GERMANY 75529/01, Grässer / Germany EGMR 66491/01,
Sedef / Germany C-230/03.
- Violation of Article 8
(Family life) of the ECHRFF 14
- CASE OF NIEMIETZ v. GERMANY, 13710/88, 16/12/1992
- CASE OF ELSHOLZ v. GERMANY, 13/07/2000, 25735/94
- CASE OF SAHIN v. GERMANY, 11/10/2001, 30943/96
- CASE OF SOMMERFELD v. GERMANY, 11/10/2001, 31871/96
- CASE OF HOFFMAN v. GERMANY, 11/10/2001, 34045/96
- VON
HANNOVER v. GERMANY, 24.06.2004, 317a(2004)
- GÖRGÜLÜ v. GERMANY, 26.02.2004, 74969/01
- Storck
v. Germany (application no. 61603/00)
- HAASE v. Germany (application no. 11057/02)
- Zaunegger v. Germany (application no. 22028/04)
CEED
- Conseil Européen des Enfants du Divorce. Parents, children and
grandparents victims of international and administrative child
abductions 22
Washington Post, 31.01.2002: Does Germany Condone Kidnapping?
Child
Abuse and Violence in German Familiy Court Practice
2004: Polish father not allowed to speak polish to his
daugthers.
2006: Petitions to European Parliament.
Germany:
Child Abduction, Hague Convention Overview
- Article 10: Decision by the European Court of Human Rights (Fifth
Section), case of Sdruženi Jihoceské Matky v. Czech Republic,
Application no. 19101/03 of 10 July 2006.
- The Higher Administrative Court in Schleswig-Holstein (see
judgement of 22. June 2005, Az: 4 LB 30/04)
ruled that to sell goods which do not meet weight requirements is a
secret not to be disclosed: ""Consumer protection is not of
constitutional rank. It must step back because ownership (Art. 14 of
the Basic Law) is protected by the constitution. Therefore ownership
is in this case stronger." The application of access to public
documents showing what authorities have measured was turn down although
there is a Freedom of Information law in force in the state of
Schleswig-Holstein. The Higher Administrative Court is
no good advertise for Germany. According to the Federal constitution protection law
§ 4 (2) there are "Among the
liberal democratic basic order in the sense of this law (...): g)
those human rights which are part of the Basic Law". Since access to
documents is missing in the German Basic Law (Constitution), it is
neccessary to add this human right in order to give Germans the same
human rights as citizens in other civiliezed countries.
- The Aarhus Convention grants the
public rights and imposes on Parties and public authorities
obligations regarding access to information and public participation
and access to justice. Germany did not ratify (April 2005) and declared:
The text of the Convention raises a number of difficult questions
regarding its practical implementation in the German legal system
which it was not possible to finally resolve during the period
provided for the signing of the Convention. These questions require
careful consideration, including a consideration of the legislative
consequences, before the Convention becomes binding under
international law.
The Federal Republic of Germany assumes that implementing the
Convention through German administrative enforcement will not lead
to developments which counteract efforts towards deregulation and
speeding up procedures.
- The German Constitutional Court often does not
give reasons e. g. in case 1
BvR 1057/02 7 about Freedom of Information 8and violates Article 6 of the ECHRFF
9
. The same problem exists for Petitions 10, there is no right to a fair answer (1 BvR 1553/90)
11. Here is an
investigation who
is responsible for the lack of freedom of information 15 in Germany.
- Access to information is limited for patient
files. A violation of Article 19 of the ICCPR. Who is responsible that patient rights are insufficient
in Germany? 12
- Watchdog documents violations of Human Rights. 17
- The highest Court in the German land
Rhineland-Palatinate LG
Mainz (1 QS 25/98) 13 stated that the court can not give access to
documents (as human rights would demand), because it is the
parliament, which would have to give this right. Germany violates Article
46 of the European Convention of Human Rights
to obey judgments.
- The forced membership in the
German lawyers bar (Rechtsanwaltskammer) violates Article 20 (2) of
the UN
Declaration of Human Rights ("No one may
be compelled to belong to an association."). Lawyers who are
critical to the German legal system can be fired from the bar with
the help of a monopoly dating back to a law on legal advice from 1935,
which means a Berufsverbot. The German bar
(Bundesrechtsanwaltskammer) is the secessor (see § 233 BRAO), of the Reichs-bar
(Reichs-Rechtsanwaltskammerder) from 18. March 1933 and constituted
(Reich-Rechtsanwaltsordnung) on 13. December 1935. The lawyers bar
in Cologne tries (See Krumbiegel Scandal)
to fire a lawyer, who promotes
Human Rights and his clients interests in clear words. Many citizens protest: Solidarity with RA Claus Plantiko: (click and add
line shift) Letter to lawyers bar (Rechtsanwaltskammer). Here is an intervention.
“Human rights” refer to those fundamental
rights and freedoms essential for human survival, liberty and
dignity that have been recognised by the global community and
protected by international legal instruments. Human rights are
universal. They are the birth-right of every man, woman and child.
Result: The Executive, Legislative, and Judicial branches in
Germany do not give a guarantee to
always support human rights (That
were the words the state used against critics). The TREATY
ON
EUROPEAN UNION, European
Convention
on Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms (ECHRFF),
International
Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR)
and the Charter
of
Fundamental Rights of the EU are not followed.
According to Article
20
Basic
Law: "All state authority is derived from the people." and "the
executive and the judiciary shall be bound by law" (given by parliament
elected by the people) "and justice". Therefore in Germany a democracy
of European type is possible, if members of parliament want it and go
for it.
The Human Rights Commissioner of the Council of Europe promised to
look through the material in the context of
a visit: http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/coe-031128.htm.
But who will invite him: the
government, the Committee
of Petitions, the Committee
of Human Rights, the Deutsche
Institut für Menschenrechte (Human Rights Institut), the
Forum für Menschenrechte or the
UN?
Do you know more? Please do not hesitate to
contact
me.
Copy sent to: Bundeskanzler, Bundespräsident,
Bundestagspräsident, Verfassungsgericht, German
Human
Rights Commissioner, 26. October 2003, German
Ministry of Justice (27. October 2003), Committee
for
Human Rights (1. November 2003),
Klaus Stoltenberg (BMJ), Ltd. Regierungsdirektor Detlef Brandner
(Regierungspräsidium
Karlsruhe), hessischer Innenminister
Volker
Bouffier, hessische Kultusministerin Karin Wolff, Federal
Administrative Court,
German
Helsinki
Committee for Human Rights, 12 states
(länder) without Freedom of Information (2005)
PS: Strasbourg, 11 July
2007 CommDH(2007)14:
REPORT
BY THE COMMISSIONER FOR HUMAN RIGHTS MR THOMAS HAMMARBERG ON HIS
VISIT TO GERMANY 9 – 11 and 15 – 20 October 2006,
https://wcd.coe.int/ViewDoc.jsp?Ref=CommDH(2007)14&Language=lanEnglish Deutsche Institut für
Menschenrechte mit der Beobachtung der Menschenrechte in Deutschland
beauftragen, nationalen "Aktionsplan Menschenrechte" entwickeln.
Enclosure:
- http://www.forumjustizgeschichte.de/Verfahren_Goetz.136.0.html
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/bockmann_nazi_law.htm
- http://www.rae-dammann.de/aktuell/vogt_germany.shtml
- http://www.berufsverbote.de/docs/hh-dammann.html
- http://www.heise.de/tp/deutsch/special/frei/12314/1.html, http://www.article19.org/pdfs/publications/south-asia-foi-survey.pdf
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/petition_un.htm and http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/un-0509.htm
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/020621bvg.pdf
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/v-klage_en.htm and http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/verfassungsbeschwerde-en.htm
- http://www.justizskandale.de/1/schoeler_bverfg.html
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/030310bvg-en.htm
- http://dejure.org/gesetze/rechtsprechung/Hollerlanderschliessung.html
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/anklage.htm
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/lg_mainz-en.htm, http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/lg_mainz.htm
- http://hudoc.echr.coe.int/hudoc/default.asp?Language=en&Advanced=1
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/I_accuse.htm
- http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/de_legal_advice_law_overview.htm
- http://www.crc-watchdog.org/content/europe/violate.html
- Case Walter Keim vs. Federal
Republic of Germany VG 2 A 85.04: http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/verwaltungsgericht-en.htm
- EUCARS ( European Corruption Analysis and Reduction Service ): http://www.eucars.de/
- Toby Mendel: Freedom of
Information as an Internationally Protected Human Right, http://www.juridicas.unam.mx/publica/rev/comlawj/cont/1/cts/cts3.htm und http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/Mendel-627.htm
- The Human Rights Commissioner
writes 28. November
2003, to review the material in the context of a visit:
http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/coe-031128.htm.
- CEED - Conseil Européen des Enfants du Divorce. Parents,
children and grandparents victims of international and
administrative child abductions
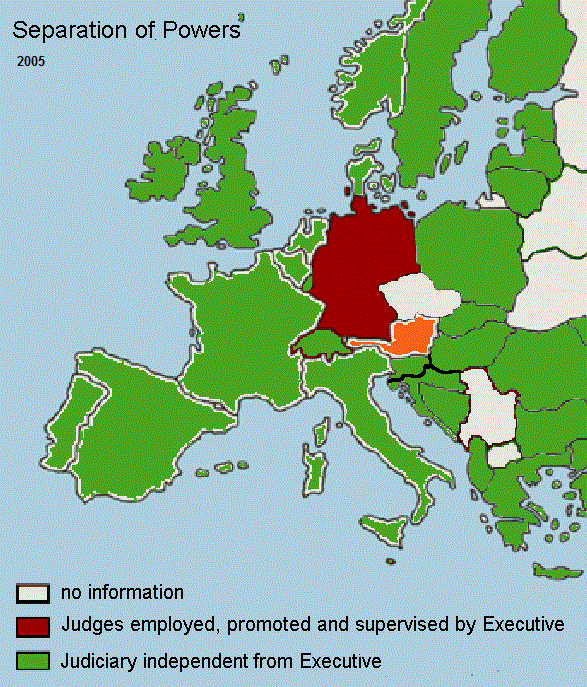
- Sepatation of powers: http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/separation_of_powers.htm
- Germany asked to remove the human right of access to public
documents and other human rights: http://wkeim.bplaced.net/files/German_comments_on_Draft_General_Comment_No.34.pdf
- HUMAN RIGHTS COMMITTEE. DISCUSSIONS ON DRAFT
GENERAL COMMENT NO. 34- MEETING NOTES (18 MARCH – 24 MARCH 2011): http://freedominfo.org/documents/HRCnotesMarch2011.pdf
Visitor No.  since
22.
October 2003
since
22.
October 2003
[Back to
page on Freedom of Information]
[Patients Rights in
Europe] [Law on Legal Advice]
[Petitions] [Back
to Homepage]
since
22.
October 2003